In recent years, the demand for energy management in households has been steadily increasing. Especially after families install photovoltaic (solar) systems, many users are opting to convert their existing grid-connected solar systems into home energy storage systems in order to enhance energy efficiency and reduce electricity costs. This conversion not only increases the self-consumption of electricity but also enhances the household’s energy independence.
1. What is a Home Energy Storage System?
A home energy storage system is a device designed specifically for household use, typically combined with a home photovoltaic system. Its primary function is to store excess electricity generated by solar power in batteries for use during nighttime or during peak electricity price periods, reducing the need to purchase electricity from the grid. The system consists of photovoltaic panels, storage batteries, inverters, and other components that intelligently regulate the supply and storage of electricity based on household consumption.
2. Why Would Users Install Energy Storage Systems?
- Saving on Electricity Bills: Household electricity demand typically peaks at night, while photovoltaic systems generate power mainly during the day, creating a mismatch in timing. By installing an energy storage system, excess electricity generated during the day can be stored and used at night, avoiding higher electricity prices during peak hours.
- Electricity Price Differences: Electricity prices vary throughout the day, with higher prices usually at night and lower prices during the day. Energy storage systems can charge during off-peak times (e.g., at night or when the sun is shining) to avoid purchasing electricity from the grid during peak price times.
3. What is a Grid-Connected Household Solar System?
A grid-connected solar system is a setup where the electricity generated by household solar panels is fed into the grid. It can operate in two modes:
- Full Grid Export Mode: All electricity generated by the photovoltaic system is fed into the grid, and users earn income based on the amount of electricity they send to the grid.
- Self-Consumption with Excess Export Mode: The photovoltaic system prioritizes supplying the household’s electricity needs, with any excess power exported to the grid. This allows users to both consume electricity and earn income from selling surplus energy.
4. Which Grid-Connected Solar Systems Are Suitable for Conversion to Energy Storage Systems?
If the system operates in Full Grid Export Mode, converting it to an energy storage system is more difficult due to the following reasons:
- Stable Income from Full Grid Export Mode: Users earn a fixed income from selling electricity, so there is less incentive to modify the system.
- Direct Grid Connection: In this mode, the photovoltaic inverter is directly connected to the grid and does not pass through household loads. Even if an energy storage system is added, excess power would only be stored and fed into the grid, not used for self-consumption.
In contrast, grid-connected systems that operate in the Self-Consumption with Excess Export Mode are more suitable for conversion to energy storage systems. By adding storage, users can store electricity generated during the day and use it at night or during power outages, increasing the proportion of solar energy used by the household.
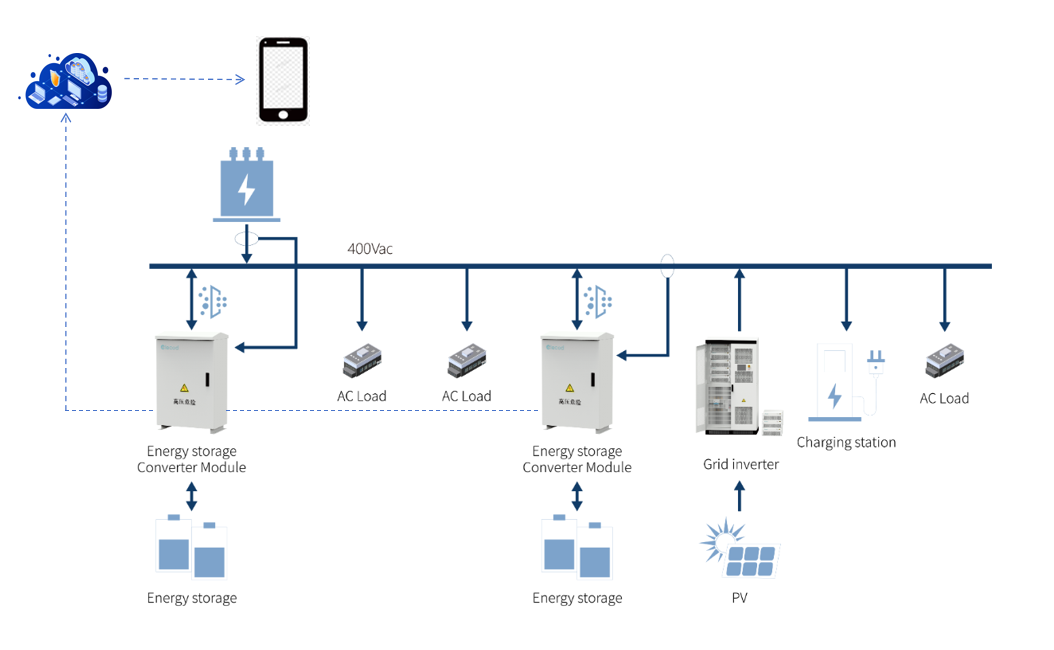
5. Conversion and Working Principles of the Coupled Photovoltaic + Energy Storage System
- System Introduction: A coupled photovoltaic + energy storage system typically consists of photovoltaic panels, grid-connected inverters, storage batteries, AC-coupled energy storage inverters, smart meters, and other components. This system converts the AC power generated by the photovoltaic system into DC power for storage in the batteries using an inverter.
- Working Logic:
- Daytime: The solar power first supplies the household load, then charges the battery, and any surplus electricity can be fed into the grid.
- Nighttime: The battery discharges to supply the household load, with any shortfall supplemented by the grid.
- Power Outage: During a grid outage, the battery only supplies power to off-grid loads and cannot supply power to grid-connected loads.
- System Features:
- Low-Cost Conversion: Existing grid-connected photovoltaic systems can be easily converted to energy storage systems with relatively low investment costs.
- Power Supply During Grid Outages: Even during a grid power failure, the energy storage system can continue to provide power to the household, ensuring energy security.
- High Compatibility: The system is compatible with grid-connected solar systems from different manufacturers, making it widely applicable.
Conclusion
By converting a household grid-connected photovoltaic system into a coupled photovoltaic + energy storage system, users can achieve greater self-consumption of electricity, reduce dependence on grid electricity, and ensure power supply during grid outages. This low-cost modification enables households to make better use of solar energy resources and achieve significant savings on electricity bills.
